STIs and HIV
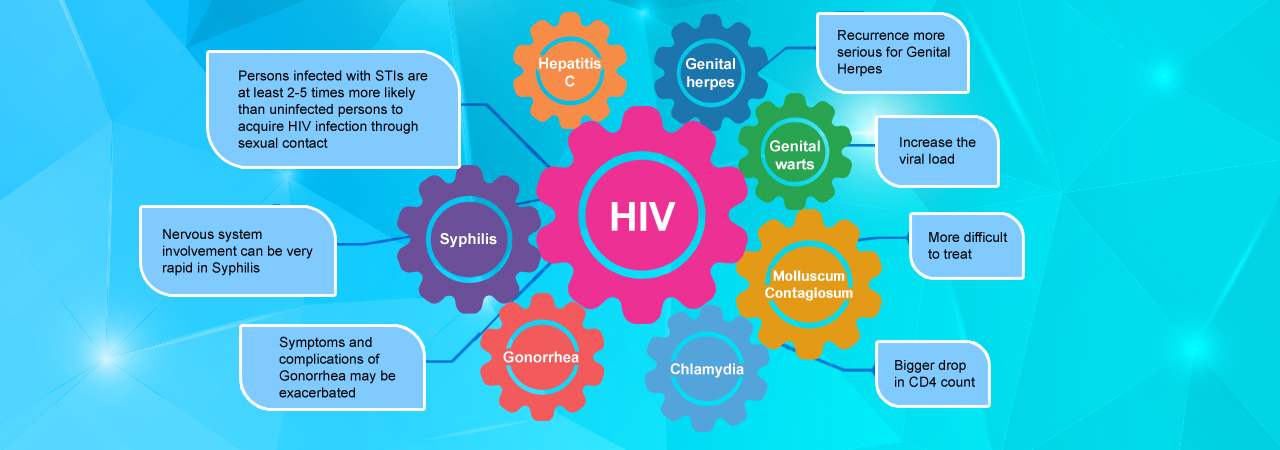
Persons infected with STDs are at least two to five times more likely than uninfected persons to acquire HIV infection if they are exposed to the virus through sex contact. In addition, persons co-infected with HIV and STI are more likely to transmit HIV to others through sex contact.
Syphilis & HIV
-
- The progression from early syphilis to nervous system involvement can be very rapid in HIV-positive men, compared to the years or decades it takes in HIV negative men. The complications to the nervous system may also occur in the early stage of infection, not just in the later stages.
- Co-infection may result in a more rapid onset of HIV disease and AIDS. It can decrease the CD4 count while increasing the viral load of HIV-positive people.
Gonorrhea & HIV
-
- Symptoms and complication of gonorrhea may be exacerbated in HIV positive men.
- Gonorrhea infection increases the amount of HIV in semen, meaning a higher chance of passing HIV on through unprotected anal sex.
- Gonorrhea, particularly anal gonorrhea, also causes inflammation which can make an HIV-negative person more susceptible to being infected with HIV.
Genital warts & HIV
-
- Genital warts may grow faster when the immune system is weakened. Anal and genital warts may also respond more slowly to the conventional topical treatment in HIV-positive men.
Genital herpes & HIV
-
- HIV-positive men may experience recurrent genital herpes more seriously than HIV-negative people. Herpes may also increase the replication of HIV and hence raising the viral load.
Chlamydia & HIV
-
- Chlamydia greatly increases the viral load in semen in HIV-positive men, meaning that it is easier to pass HIV on to others while you have chlamydia.
Hepatitis C & HIV
-
- A person who is co-infected can have increased HIV viral load. Moreover, untreated HIV may cause a rise in hepatitis C viral load. Some people do need to be treated for both infections.
- People with both HIV and hepatitis C are advised to monitor the liver enzyme level regularly, and avoid HAART most strongly associated with liver problems.
Molluscum Contagiosum & HIV
-
- The risk of getting molluscum is higher in those with HIV. Bumps may be anywhere on the body but are often on the face. It is more difficult to give an effective treatment to HIV-infected people than to HIV-negative ones.